Consulting a Plastic Surgeon for a Complete Transformation
October 1, 2025
The Significance of Ultrasound in Obstetric Care
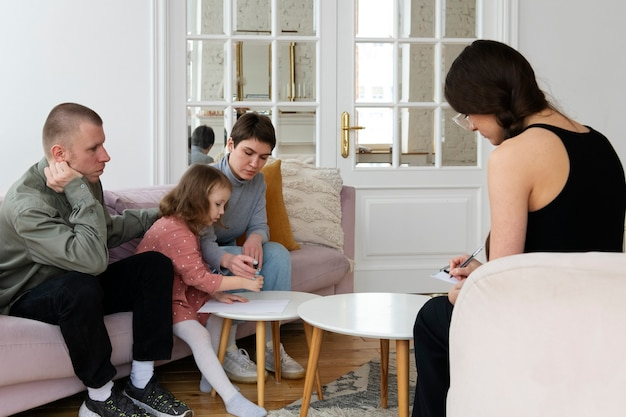
October 1, 2025While occasional worries are a normal part of growing up, persistent or overwhelming anxiety can interfere with school, relationships, and daily life. Recognizing the signs early and providing the right support is fundamental for long-term well-being. Here’s more information on anxiety in young people:
Understanding Anxiety in Young People
Anxious feelings are emotions that everyone experiences at times. When anxious feelings become excessive worry that interferes with daily functioning, it may indicate an anxiety disorder. Young people can develop various types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety, and separation anxiety.
Children and adolescents process emotions differently from adults. Their developing brains may struggle to regulate anxious feelings effectively. Environmental factors, such as school stress, family changes, or peer pressure, can trigger or exacerbate symptoms. Biological factors also play a role, as these disorders often run in families.
The key difference between normal anxious feelings and problematic anxiety lies in duration, intensity, and impact on functioning. Normal anxious feelings are temporary and related to specific situations. Anxiety disorder persists over time and significantly affects a young person’s ability to participate in age-appropriate activities.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms
Identifying anxiety in children and adolescents requires careful observation of behavioral, physical, and emotional changes. Young people may not always verbalize their anxious feelings, making it helpful to watch for specific indicators. Here are the key signs and symptoms associated with anxiety:
- Physical Symptoms: Physical symptoms often include headaches, stomachaches, fatigue, muscle tension, and changes in sleep patterns. Children may frequently complain of feeling unwell or have difficulty falling asleep. Some young people experience rapid heartbeat, sweating, or trembling during anxious episodes.
- Behavioral Signs: Behavioral signs include avoidance of certain activities, excessive need for reassurance, difficulty concentrating, and changes in academic performance. Adolescents may withdraw from social activities and refuse to attend school.
- Emotional and Mood Changes: Children may display irritability and mood swings. Some children develop repetitive behaviors or rituals that they believe will reduce their anxious feelings
Recognizing these patterns in children and adolescents is key to early intervention.
Addressing Anxious Feelings
Several evidence-based approaches can help young people manage their anxiety effectively. Here are some of them:
- Create a Supportive Environment: Establishing a nurturing environment at home and school forms the foundation for successful management. This includes offering reassurance, validating feelings, and promoting open communication.
- Teach Relaxation Techniques: Providing children with practical tools such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness activities can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Introduce Cognitive Strategies: Teaching children to recognize negative thinking patterns and replace them with balanced, constructive thoughts reduces excessive worry.
- Implement Gradual Exposure: Encourage gradual exposure to feared situations, starting with less threatening scenarios and progressing to more challenging ones.
By adopting these strategies, parents, caregivers, and educators can equip children and adolescents with the skills needed to manage anxiety and improve overall well-being.
Seeking Professional Help
Professional intervention becomes necessary when anxiety significantly impairs a young person’s functioning across multiple areas of life. If anxious feelings persist for several weeks despite supportive interventions, consulting with a psychiatrist or mental health professional is recommended.
Signs that indicate the need for professional help include severe avoidance behaviors, panic attacks, persistent physical symptoms without a medical cause, and a significant decline in academic or social functioning. Young people who express thoughts of self-harm or exhibit extreme distress require immediate professional attention. Mental health professionals can provide specialized treatments and determine if other conditions are contributing to the symptoms.
Schedule Your Anxiety Consultation Today
Addressing anxiety in children and adolescents requires patience, understanding, and appropriate interventions. Early recognition of symptoms and implementation of effective strategies can significantly improve outcomes for young people experiencing anxious feelings. If you notice persistent signs of anxiety in your child, contact a psychiatrist near you today to schedule a consultation and explore treatment options.



