Insemination for LGBTQ+ Couples: What Are the Options?
September 8, 2025
Navigating Prostate Cancer: The Power of a Second Opinion for Informed Choices
September 9, 2025Infertility occurs when a woman cannot become pregnant after trying for a year without using protection and having regular intercourse. For women over 35, this timeline may be adjusted to six months. There are various treatments to address the different causes of infertility. Here’s some information about these treatment options and when to use them:
Oral Medications
Fertility medications typically serve as the initial treatment approach. These drugs are designed to stimulate the ovaries to produce one or more eggs per cycle, a process known as ovulation induction. The goal is to increase the likelihood of releasing an egg available for fertilization.
Clomiphene citrate is an oral medication that encourages the body to produce more of the hormones responsible for egg maturation and release. For many patients, Clomiphene citrate serves as a first-line treatment option due to its effectiveness, ease of use, and benefits. Doctors may also use other classes of medications.
A doctor monitors your progress through blood tests and ultrasounds to track follicle development and to time intercourse or subsequent procedures appropriately. These treatments aim to significantly improve the chances of conception. Work closely with a healthcare provider so they can adjust the approach to your specific needs.
Assisted Reproductive Technology
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) refers to a group of procedures that involve handling both eggs and sperm. Doctors use these methods when other treatments have not been successful or for specific types of infertility diagnoses. ART procedures provide assistance at various stages of conception, from fertilization to implantation. The specific type of ART recommended will depend on your individual circumstances and medical history.
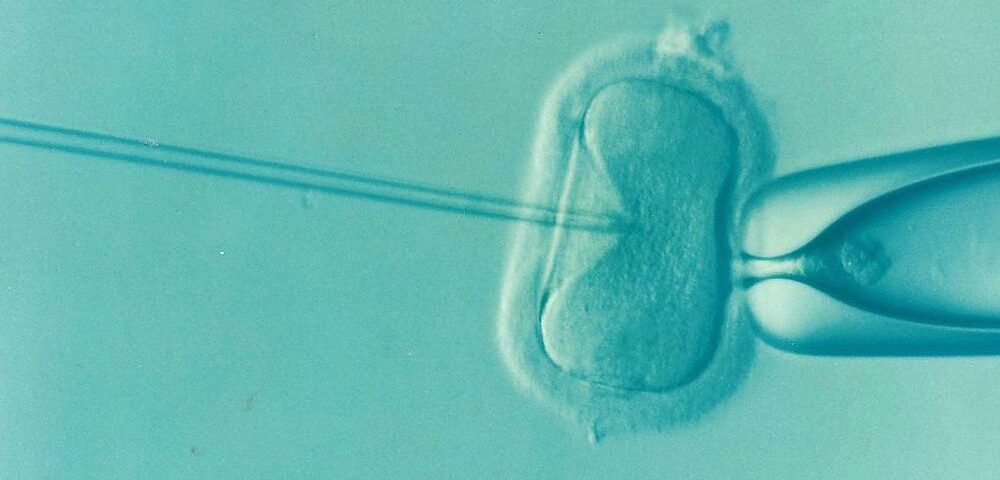
In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a practical ART procedure that involves several steps. First, doctors typically use medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. They can then retrieve these eggs from the ovaries through a minor surgical procedure.
In the laboratory, the healthcare team may combine the retrieved eggs with sperm to facilitate fertilization. The resulting embryos grow and develop as doctors monitor them for several days. Finally, doctors can transfer one or more healthy embryos into the uterus, hoping that one will implant and lead to a pregnancy. They may freeze additional healthy embryos for future use.
Intrauterine Insemination
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is less invasive than IVF. A medical team typically collects, concentrates, and prepares sperm in a laboratory. They may use a thin, flexible catheter to place the prepared sperm directly into the uterus.
Doctors typically time this procedure to coincide with ovulation, which can occur naturally or be induced with medication. Placing the sperm closer to the fallopian tubes may increase the chances of sperm reaching the egg, improving the likelihood of fertilization. Doctors may recommend IUI for couples experiencing unexplained infertility or other issues.
Get Treated for Infertility
A specialist can provide a detailed evaluation of your reproductive health and offer personalized guidance based on your specific needs. They can explain each option, discuss the steps involved, and help you understand what to expect. If you are ready to explore your options, schedule a consultation with a fertility team. Contact a physician today to learn more about how treatments can help you.