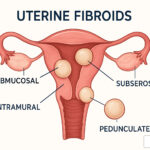
The Importance of Gynecology in Managing Uterine Health
September 9, 2025
Disc Replacement Surgery Recovery Protocols
September 9, 2025An obstetrician-gynecologist (OBGYN) is a medical doctor focused on female reproductive health, which includes pelvic health. Pelvic health refers to the well-being of the pelvic floor muscles and the organs they support, including the bladder, uterus, and rectum. Here is more information on how an OBGYN evaluates pelvic health, manages common conditions, and provides preventative care guidance:
Evaluating Pelvic Health
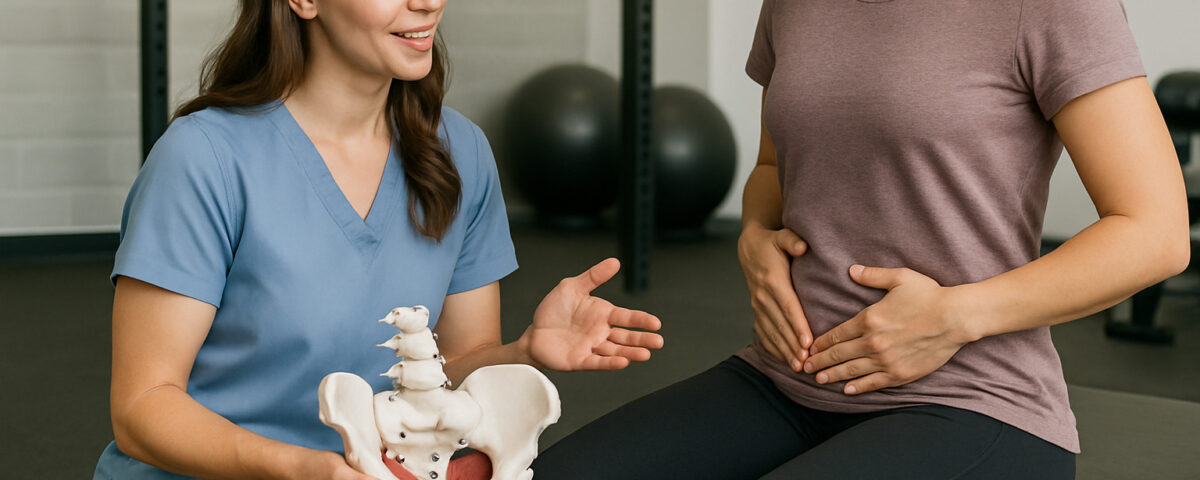
An OBGYN starts with a comprehensive assessment to understand pelvic health. The visit begins with a detailed medical history. The doctor asks about symptoms like changes in bladder or bowel function, feelings of pelvic pressure, or pain during activities such as exercise or intercourse. These questions help identify any issues that might affect pelvic health.
Following the history, a physical pelvic exam takes place. The physician examines the pelvic organs and assesses the strength and tone of the pelvic floor muscles. Patients may be asked to cough or bear down while the doctor observes for pelvic organ movement or urine leakage. This approach helps identify anatomical changes or muscle weakness that are responsible for the symptoms. Results from this evaluation guide further diagnostic tests or a management plan.
Managing Common Pelvic Conditions
OBGYNs frequently address conditions such as pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the supporting muscles and ligaments of the pelvic organs weaken, allowing organs to drop or push into the vagina. Management depends on severity and specific symptoms. Non-surgical options often include pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegels) to strengthen muscles. Some patients benefit from using a pessary, a removable device that supports the pelvic organs within the vagina.
Urinary incontinence, or the involuntary loss of urine, is another issue that OBGYNs help address. The physician first distinguishes between types of incontinence, such as stress (leakage with activity), urge (sudden, strong urge to urinate), or mixed. For stress incontinence, pelvic floor exercises can help improve muscle strength and bladder control. For urge incontinence, bladder training and behavioral strategies may be helpful. An OBGYN develops a management plan that matches the patient’s diagnosis and lifestyle needs.
Providing Care and Education
Preventive care forms a central part of OBGYN practice, as physicians offer guidance to support long-term pelvic health. This guidance often focuses on teaching correct techniques for pelvic floor muscle exercises, which help maintain muscle tone and prevent symptoms from worsening. Doctors also discuss the benefits of maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the pelvic floor.
Education includes information about changes that can occur over a woman’s life, such as pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause. These life stages might affect pelvic floor support, as hormonal changes and physical stresses contribute to muscle and ligament changes. OBGYNs provide clear explanations, so patients can recognize early signs of pelvic floor dysfunction and seek care quickly. This proactive approach helps women protect their pelvic health throughout different life stages.
Find an OBGYN
An OBGYN delivers thorough and structured care for a wide range of pelvic health concerns. The process begins with a full evaluation, which includes a medical history and a physical exam. OBGYNs manage issues like pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence using individualized, non-surgical approaches. Preventative education and ongoing guidance help patients maintain pelvic floor health as they move through life. If you’re due for a visit, contact a qualified OBGYN.