Common Misconceptions About Glaucoma
February 20, 2026
The Role of Bulk Posting on Google My Business for Brand Growth
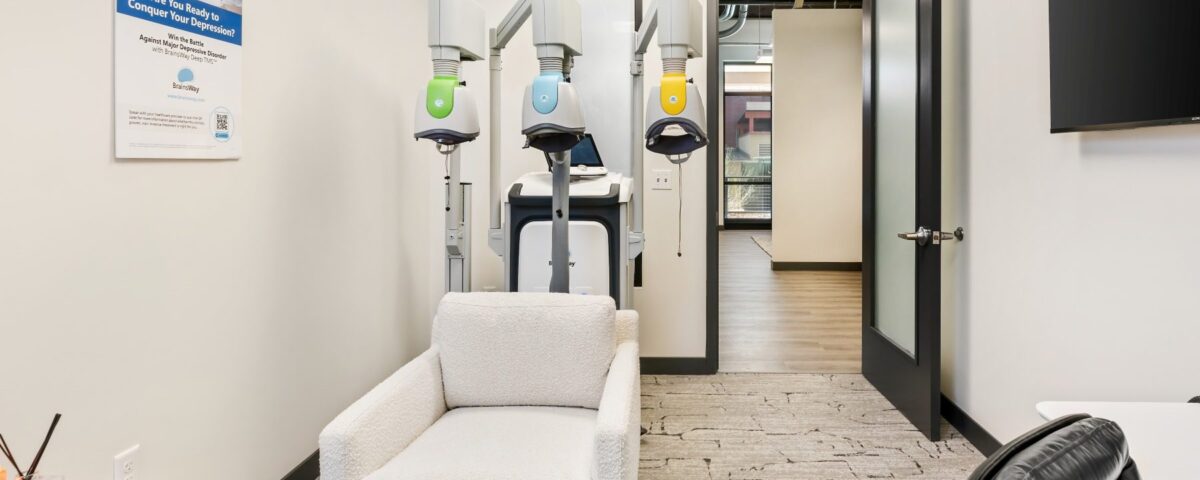
February 20, 2026Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. The brain relies on electrical and chemical signals to function, and in conditions like depression, certain areas of the brain may be underactive. This treatment is used when other treatments haven’t been effective for certain mental disorders. During a therapy session, an electromagnetic coil is placed against the head. Here’s information on TMS therapy and how it may benefit mental conditions like depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD):
What Is Treatment-resistant Depression?
Major depressive disorder is a common mood disorder that causes persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest. While many individuals find relief through standard treatments like medication and psychotherapy, some do not experience significant mental health improvement. Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) occurs when someone has tried at least two different antidepressants from different classes without much effect. Symptoms continue to persist, or they may improve briefly before returning. TRD can be frustrating, but alternative treatments like TMS offer another avenue for potential symptom relief.
Why Is This Therapy Recommended?
TMS therapy is a non-systemic treatment, so it doesn’t circulate in the bloodstream as medication does. It is often recommended for adults who have not benefited from prior interventions. TMS therapy is FDA-cleared for treating major depressive disorder and OCD, usually part of a larger comprehensive plan.
How Does TMS Treat Mental Illness?
TMS therapy targets the prefrontal cortex, a specific area of the brain known to regulate mood. The magnetic pulses stimulate neurons, causing them to fire. This repeated stimulation is shown to strengthen the connections between nerve cells. This increased activity can help reset the brain’s mood-regulating networks, potentially leading to a reduction in challenging symptoms.
What Is Treatment-resistant OCD?
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a chronic condition where a person has uncontrollable, recurring thoughts (obsessions) and behaviors (compulsions). Like depression, OCD is typically treated with prescription medication and therapy, often utilizing medications and cognitive behavioral therapy. Nearly half of the people with OCD do not respond adequately to these standard first-line treatments. When standard therapies fail to reduce the severity of obsessions and compulsions, the condition is seen as treatment-resistant.
How Does TMS Therapy Work?
A typical TMS therapy session is an outpatient procedure performed in a medical office or clinic. You will sit in a reclining chair, and a technician will place a magnetic coil against your head after giving you ear protection. When the machine is turned on, you will hear loud clicking sounds and feel a tapping sensation on your forehead.
You remain awake and alert during the entire procedure, and no anesthesia is required. Because there is no sedation involved, you can drive yourself home immediately after the appointment and resume normal daily activities. A standard course of treatment involves sessions five days a week for several weeks, but providers may recommend recurring treatments for some conditions.
Contact a Mental Health Specialist Today
If you have not found relief through traditional medications, it may be time to explore other options. TMS therapy offers a non-invasive alternative that targets specific areas of the brain. This therapy delivers a magnetic pulse, stimulating nerve cells in your frontal cortex to improve mood regulation and reduce symptoms. Navigating mental health concerns can be challenging, but specialized care is available to support you. Contact a mental health specialist to learn more about your treatment options.